page 33
Note: the contents of this page as well as those which precede and follow, must be read as a continuation and/or overlap in order that the continuity about a relationship to/with the dichotomous arrangement of the idea that one could possibly talk seriously about peace from a different perspective as well as the typical dichotomous assignment of Artificial Intelligence (such as the usage of zeros and ones used in computer programming) ... will not be lost (such as war being frequently used to describe an absence of peace and vice-versa). However, if your mind is prone to being distracted by timed or untimed commercialization (such as that seen in various types of American-based television, radio, news media and magazine publishing... not to mention the average classroom which carries over into the everyday workplace), you may be unable to sustain prolonged exposures to divergent ideas about a singular topic without becoming confused, unless the information is provided in a very simplistic manner.
Let's face it, humanity has a lousy definition, accompanying practice, and analysis of peace.
If we view War as a disease, is it appropriate for us to view Peace in terms of being a cure? Or is peace but a momentary remission of symptoms that can flare up at any time... or on a schedule we have not as yet been able to accurately catalog? And does the presumed "cure" come with its own sort of problems if it is used too long... like some medicines whose prolonged use and/or dosage has a limit before toxicity sets in?
While many of us might agree that war is a disease, accident or injury, could it be but the raw, the undomesticated, the primitive expression of something that can be transformed into something of greater value because it incorporates a developmental ability that is absent in peace? If peace is in its most ultimate form of development, that it can not be anything but what it is in its present form and application, does it lack adaptability to improve as the species improves, and will it act as a constraint? ...Like a parental figure who is ideally suited to assist young children in their development, but are less helpful when the children mature into young adults who have acquired a university level of education and experiences. So long as humanity retains some measure of a particular type of innocence and ignorance, the idea of peace as it is presently conceived (largely in terms of being a polar opposite to war); will be sufficient. No less, the present idea(s) of war or conflict may likewise impose restrictions on the developmental character of humanity. For example, if a species defines war in terms of using sticks and rocks; a war that is defined by using spears and arrows is a different species of war. Likewise if peace is defined in one way according to the conditions of a given people in one environment, and then defined in another way in a different setting. Such examples can be understood by those making an analogy between what one person views as junk, another may well view as a treasure.
If a person can only recognize peace as a momentary respite in the midst of a war, is this the same for those who identify war in contrast to their presumed presence in a perspective of peace? Is war a disease or pothole in the road? Is peace a cure or merely a bandaid? Is war an uphill climb and peace a downhill coast? Are all our analogies rather naive interpretations? If war spurs innovation, is the innovation of lasting value to human progress, or only gives the impression of progress along a singular path... like a speciality tool designed for a given purpose and has no readily apparent application elsewhere? If we identify war as a type of infection, which disease is most useful in providing a description that best provides an analogy as to its occurrence and effects? Because malaria occurs in cycles, has been around for thousands of years, and is intermittently treated... from which is obtained different results for different kinds of malarial infections, it may be a good model if we consider war, and peace, to be different types of infections, or parasites, or treatments. The following article about malaria needs to be viewed from the perspective of being a metaphor that describes the peace/war circumstance. The first paragraph is followed by a rendering which displays the application of the contents into a "war" framework, even though it does not give details about war-mongering parasites, breeding environments, delayed intervention efforts, etc...:
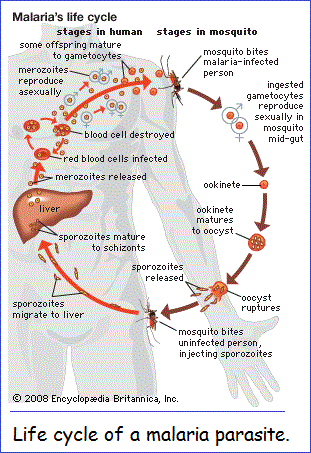
(Malaria is a) serious relapsing infection in humans, characterized by periodic attacks of chills and fever, anemia, splenomegaly (enlargement of the spleen), and often fatal complications. It is caused by one-celled parasites of the genus Plasmodium that are transmitted to humans by the bite of Anopheles mosquitoes. Malaria can occur in temperate regions, but it is most common in the tropics and subtropics. In many parts of sub-Saharan Africa, entire populations are infected more or less constantly. Malaria is also common in Central America, the northern half of South America, and in South and Southeast Asia. The disease also occurs in countries bordering on the Mediterranean, in the Middle East, and in East Asia. In Europe, North America, and the developed countries of East Asia, malaria is still encountered in travelers arriving or returning from affected tropical zones.
War is a serious relapsing infection is humans, characterized by periodic attacks, and often fatal complications. War can occur in temperate regions, but can occur just about anywhere. In many parts of the world, entire populations are infected more or less constantly. War is also common in the Americas, Europe and Asia, though it may be otherwise labeled to distinguish internalized protests with or without the presence of military armaments. The ravages of war and its effects can sometimes be encountered in travelers arriving or returning from affected war zones.
In the early 21st century the incidence of malaria, and the number of deaths caused by the disease, appeared to be declining. For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that in 2000 there were 233 million cases of malaria worldwide, with roughly 985,000 deaths resulting—most of them young children in Africa. In 2009 there were an estimated 225 million cases and 781,000 deaths, and in 2010 there were an estimated 216 million cases and 655,000 deaths. A predictive modeling analysis of death trends over time that was published by a team of U.S. and Australian scientists in the journal Lancet in early 2012 suggested that, while a trend toward fewer deaths had emerged, globally, deaths from malaria were far higher than the WHO estimates. That analysis revealed an estimated increase in deaths from 995,000 in 1980 to 1,817,000 in 2004, followed by a decline to 1,238,000 in 2010.
The course of the disease
Malaria in humans is caused by five related protozoan (single-celled) parasites: Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and P. knowlesi. The most common worldwide is P. vivax. The deadliest is P. falciparum. In 2008 P. knowlesi, which was thought to infect primarily Old World monkeys and to occur only rarely in humans, was identified as a major cause of malaria in humans in Southeast Asia, accounting for as many as 70 percent of cases in some areas. P. knowlesi was found to be easily confused with P. malariae during microscopic examination, resulting in many cases being attributed to P. malariae when in fact they may have been caused by P. knowlesi.
Plasmodium parasites are spread by the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes, which feed on human blood in order to nourish their own eggs. While taking its meal (usually between dusk and dawn), an infected mosquito injects immature forms of the parasite, called sporozoites, into the person's bloodstream. The sporozoites are carried by the blood to the liver, where they mature into forms known as schizonts. Over the next one to two weeks each schizont multiplies into thousands of other forms known as merozoites. The merozoites break out of the liver and reenter the bloodstream, where they invade red blood cells, grow and divide further, and destroy the blood cells in the process. The interval between invasion of a blood cell and rupture of that cell by the next generation of merozoites is about 48 hours for P. falciparum, P. vivax, and P. ovale. In P. malariae the cycle is 72 hours long. P. knowlesi has the shortest life cycle—24 hours—of the known human Plasmodium pathogens, and thus parasites rupture daily from infected blood cells.

Most merozoites reproduce asexually—that is, by making identical copies of themselves rather than by mixing the genetic material of their parents. A few, however, develop into a sexual stage known as a gametocyte. These will mate only when they enter the gut of another mosquito that bites the infected person. Mating between gametocytes produces embryonic forms called ookinetes; these embed themselves in the mosquito's gut, where they mature after 9 to 14 days into oocysts, which in turn break open and release thousands of sporozoites that migrate to the insect's salivary glands, ready to infect the next person in the cycle.
Typically, victims who are bitten by malaria-carrying mosquitoes experience no symptoms until 10 to 28 days after infection. The first clinical signs may be any combination of chills, fever, headache, muscle ache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Chills and fever occur in periodic attacks; these last 4 to 10 hours and consist first of a stage of shaking and chills, then a stage of fever and severe headache, and finally a stage of profuse sweating during which the temperature drops back to normal. Between attacks the temperature may be normal or below normal. The classic attack cycles, recurring at intervals of 48 hours (in so-called tertian malaria) or 72 hours (quartan malaria), coincide with the synchronized release of each new generation of merozoites into the bloodstream. Often, however, a victim may be infected with different species of parasites at the same time or may have different generations of the same species being released out of synchrony—in which case the classic two- or three-day pattern may be replaced by more frequent rigours of chills, fever, and sweating. The parasites continue to multiply—unless the victim is treated with appropriate drugs or dies in the interim.
Besides attacks, persons with malaria commonly have anemia (owing to the destruction of red blood cells by the parasites), enlargement of the spleen (the organ responsible for ridding the body of degenerate red blood cells), and general weakness and debility. Infections due to P. falciparum are by far the most dangerous. Victims of this “malignant tertian” form of the disease may deteriorate rapidly from mild symptoms to coma and death unless they are diagnosed and treated promptly and properly. The greater virulence of P. falciparum is associated with its tendency to infect a large proportion of the red blood cells; patients infected with that species will exhibit ten times the number of parasites per cubic millimetre of blood than patients infected with the other three malaria species. In addition, red blood cells infected with P. falciparum have a special tendency to adhere to the walls of the tiniest blood vessels, or capillaries. This results in obstruction of the blood flow in various organs, but the consequences are gravest when capillaries in the brain are affected, as they often are. It is this latter complication—known as cerebral malaria and manifested by confusion, convulsions, and coma—that frequently kills victims of P. falciparum malaria. Several strains of P. falciparum have developed that are resistant to some of the drugs used to treat or prevent malaria.
Infections of P. vivax and P. ovale differ from the other two types of malaria in that some of the sporozoites may remain dormant in the liver in a “hypnozoite” stage for months or even years before emerging to attack red blood cells and cause a relapse of the disease.
Diagnosis and treatment
If diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms alone, malaria may easily be confused with any of several other diseases. For example, an enlarged spleen can also sometimes be caused by other less-prevalent tropical infections such as schistosomiasis, kala-azar (a type of leishmaniasis), and typhoid fever. For this reason the most reliable method of diagnosis is a laboratory test in which a trained technician is able to distinguish between the four species of parasites when a smear of blood from the infected person is examined under a microscope. The method has drawbacks, however. For example, the test is time-consuming, may fail to detect cases where there are very few parasites, and relies on a laboratory and skilled staff. Therefore, symptoms will continue to be an important clue in detecting malaria, especially for people who live in rural areas that lack sophisticated laboratory facilities but also for international travelers. Most travelers will not develop symptoms until they return home to countries where malaria may not be endemic. This makes it vital that they recognize the possible early signs of infection themselves and tell their doctors where they have been. Otherwise, their illness may be dismissed as flu, with potentially fatal consequences. In some cases, malaria can kill within hours.
An effective treatment for malaria was known long before the cause of the disease was understood: the bark of the cinchona tree, whose most active principle, quinine, was used to alleviate malarial fevers as early as the 17th century. Quinine has been extracted from cultivated cinchona trees since the early 19th century. Despite a range of side effects such as tinnitus (ringing in the ears), blurred vision, and, less commonly, blood disorders and various allergic reactions, it is still used, especially for severe malaria and in cases in which the parasites are resistant to other, newer drugs. Chief among these newer drugs are chloroquine, a combination of pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine, mefloquine, primaquine, and artemisinin—the latter a derivative of Artemisia annua, a type of wormwood whose dried leaves have been used against malarial fevers since ancient times in China. All of these drugs destroy the malarial parasites while they are living inside red blood cells. For the treatment of malignant or cerebral malaria, the antimalarial drug must be given intravenously without delay, and measures are taken to restore the red blood cell level, to correct the severe upset of the body's fluids and electrolytes, and to get rid of urea that accumulates in the blood when the kidneys fail.
In their initial decades of use, chloroquine and related drugs could relieve symptoms of an attack that had already started, prevent attacks altogether, and even wipe out the plasmodial infection entirely. By the late 20th century, however, some strains of P. vivax as well as most strains of P. falciparum had become resistant to the drugs, which were thus rendered ineffective. As a result, the incidence of malaria began to increase after having steadily declined for decades.
Unlike some infectious diseases, infection with malaria induces the human body to develop immunity very slowly. Unprotected children in tropical countries acquire sufficient immunity to suppress clinical attacks only after many months or a few years of constant exposure to Plasmodium parasites by hungry mosquitoes. Even then, the immunity is effective only against the specific parasite to which the child has been exposed, and the immunity wanes after several months if the child is removed from constant exposure. One interesting group that shows unusual resistance to malaria are carriers of a gene for the sickle-cell trait (see sickle cell anemia). Infection of the red blood cells induces the sickling effect, and the cells are destroyed along with the parasites.
In 2008 scientists reported the discovery of a group of proteins synthesized by Plasmodium that mediate the parasite's ability to make human red blood cells “sticky.” Stickiness causes the infected human cells to adhere to the walls of blood vessels, allowing the parasite to evade transport to the spleen and hence destruction by the host's immune system. Scientists found that blocking the synthesis of one of the proteins involved in mediating this adherence process renders the parasite susceptible to elimination by the host's immune system. These adherence proteins represent possible targets for the development of novel antimalarial drugs.
International efforts have been under way for decades to produce a malaria vaccine, so far without success. In order to immunize against Plasmodium, a different response must be elicited from the immune system at each of the parasites' different life-cycle stages. Moreover, the parasites' surface proteins change rapidly, so that a vaccine based on a particular “cocktail” of proteins might not necessarily protect against all forms of the parasite that the immunized person might encounter. Still, work continues on vaccines that would aim to limit or completely prevent infection by parasites by stimulating the production of antibodies to specific surface proteins. Another strategy is to develop an “antidisease” vaccine, which would block not the infection itself but rather the immune system's responses to infection, which are responsible for many of the harmful symptoms. A third approach, known as the “altruistic” vaccine, would not stop either infection or symptoms but would prevent infection from spreading to others by blocking the ability of the parasites to reproduce in the gut of the mosquito.
While the world awaits a vaccine, the mainstay of prevention in much of Africa and Southeast Asia is the insecticide-treated bed net, which has reduced mortality significantly in some areas. For example, in western Kenya the use of bed nets reduced mortality among children by 25 percent. Bed nets can be washed but must be re-treated with insecticide about every 6–12 months, depending on the frequency of washing. Long-lasting insecticide-treated nets (LLINs), in which insecticide forms a coating around the net's fibres or is incorporated into the fibres, can be used for at least three years before re-treatment is required. Frequent washing, however, may render LLINs less effective over time. In addition, a report published in 2011 concerning the use of deltamethrin-treated LLINs over a two-and-a-half-year period in Senegal revealed that some 37 percent of Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes were resistant to the insecticide. Prior to the study, only 8 percent of A. gambiae mosquitoes carried the genetic mutation responsible for resistance. Although longer-term investigations were needed to confirm the association between LLINs and insecticide resistance, the findings raised important questions for the future of malaria prevention and control. Furthermore, there were concerns that because bed nets reduced exposure to mosquito bites, the nets might also lead to reduced acquired immunity to malaria. This concern was highlighted by the marked increase in infection rates in the Senegal LLIN study.
For travelers to malarial regions, essential equipment in addition to a bed net would include a spray-on or roll-on insecticide such as diethyl toluamide. Travelers should also take antimalarial drugs prophylactically, though none is completely effective against the parasites. The most comprehensive method of prevention is to eliminate the breeding places of Anopheles mosquitoes by draining and filling marshes, swamps, stagnant pools, and other large or small bodies of standing freshwater. Insecticides have proved potent in controlling mosquito populations in affected areas.
Malaria through history
The human species has suffered from malaria for thousands of years. In ancient Egypt malaria probably occurred in lowland areas; the enlarged spleens of some Egyptian mummies are surviving traces of its presence. Tutankhamen, who reigned as king of ancient Egypt from 1333 to 1323 BCE, may have been afflicted by the disease; in 2010 scientists recovered traces of malaria parasites from the mummified remains of his blood.
In ancient Greece malaria appeared annually as an autumnal fever and was described by Hippocrates and others. Some scholars have surmised that malaria occurring in Greece in those times was probably caused by P. vivax and P. malariae. By the later classical period of the Roman Empire, however, malaria was a much more serious disease than it had previously been in the lands along the north shore of the Mediterranean Sea, and the association of malaria with the Pontine Marshes of the Roman Campagna was well established. Modern malariologists have attributed this increase in the severity of malaria to ecological changes associated with deforestation that had accompanied intensified agricultural activities—changes that allowed new species of mosquitoes from North Africa to be introduced and successfully established in southern Europe. Two of the introduced species were better transmitters of P. falciparum than any of the native European insects.
Alexander the Great, whose death on the banks of the Euphrates River in June 323 BCE was attributed to malaria, shared that fate with numerous illustrious victims. In the Italian peninsula, malaria killed Pope Innocent III as he was preparing to lead a Crusade to the Holy Land in 1216, the poet Dante Alighieri in 1321, and Pope Leo X in 1521. The artist Raphael, who painted a famous portrait of Leo X, also died of malaria (in 1520). Thirty-eight years later the former Holy Roman emperor Charles V reportedly succumbed to the disease in Spain.
Malarial fevers were associated with swamps and marshes as early as classical Greece, but the role of mosquitoes in transmitting the infection was completely unknown. Many of the early Greeks thought the disease was contracted by drinking swamp water; later, because the Romans attributed it to breathing “miasmas,” or vapours, arising from bodies of stagnant water, the disease came to be called mal aria, or “bad air.” Since early Greek times, attempts were made to control malaria by draining swamps and stagnant marshes, but a specific treatment for the disease did not become available in Europe until the 1630s, when bark of the cinchona tree was introduced into Spain from Peru. The skillful use of “Peruvian bark” by the great English physician Thomas Sydenham helped to separate malaria from other fevers and served as one of the first practices of specific drug therapy. The lifesaving drug became much more widely available by the mid-19th century, after the active ingredient of cinchona, quinine, was successfully isolated and the Dutch began to cultivate the cinchona tree in plantations on the island of Java.
Following the introduction of cinchona bark, no comparably significant advance in the understanding of malaria or its control came until after the 1870s, when pioneering studies by Louis Pasteur in France and Robert Koch in Germany laid the foundations of modern microbiology. In November 1880 Alphonse Laveran, a French military physician working in Algeria, showed that the elements seen in red blood cells of certain patients were parasites responsible for their hosts' malaria. Laveran won a Nobel Prize in 1907 in part for this discovery. In August 1897, in India, British bacteriologist Ronald Ross discovered parasites of a malaria of birds in the stomach of a Culex mosquito, and in 1898, in Rome, Giovanni Grassi and his colleagues discovered a parasite of human malaria in an Anopheles mosquito. A bitter controversy that ensued between Ross and Grassi and their respective partisans over priority of discovery was one of the most vitriolic public quarrels in modern science. (Ross was awarded a Nobel Prize in 1902.)
Immediately following the discovery that mosquitoes were the vectors for transmitting malaria to humans, William C. Gorgas, an American army surgeon, led two campaigns of mosquito reduction using sanitary measures (drainage and larviciding) in Cuba and Panama. Gorgas's campaign made the U.S. construction of the Panama Canal possible. It also made the killing of mosquito larvae by spreading oil on their breeding sites another widely accepted means of controlling the disease. In 1939–40 Fred Soper of the Rockefeller Foundation led a vigorous effort in Brazil that eradicated the Anopheles gambiae mosquito, using a dust larvicide (Paris green) against the larvae and a newly discovered insecticide (pyrethrum) against the adult insects. The entire anti-malarial effort was given an enormous boost in 1939 when the Swiss chemist Paul Müller discovered the insecticidal properties of DDT. (Müller received a Nobel Prize in 1948 for his work.) After a six-year campaign (1946–51) of spraying DDT in Sardinia, malaria virtually disappeared from that Mediterranean island. Similar success was achieved in Greece, and with that, public health officials began to contemplate the possible eradication of malaria from the globe.
Even as these multiple methods of attacking the mosquito vector were being improved, direct means of attacking the parasite itself were also refined. Chloroquine, the mainstay of modern antimalarial drugs, was first synthesized in Germany in 1934, and pyrimethamine was synthesized in the United States during World War II (1939–45) by a team that included future Nobel laureates George H. Hitchings and Gertrude B. Elion. The value of the synthetic antimalarials was heightened for the wartime Allies after Japan seized Java, where the Dutch cinchona plantations were the main source of quinine. Because the synthetics were cheaper, more plentiful, and caused fewer side effects than the natural products from bark, they too raised hopes after the war of winning a global campaign against malaria.
In 1955 the World Health Organization (WHO) inaugurated its Global Malaria Eradication Campaign, to be based mainly on the spraying of insecticide in designated "malarious areas" of the world. The program resulted in the elimination of endemic malaria from Europe, Australia, and other developed areas and in a radical reduction of cases in less-developed countries such as India. However, by 1969 WHO was forced to abandon its dream of complete eradication. Species of Anopheles mosquitoes had quickly developed resistance to DDT, and the insecticide itself fell out of favour owing to its cost and ecological effects. More disturbing was the appearance of drug-resistant strains of Plasmodium. The first chloroquine-resistant parasites emerged in the late 1950s and early 1960s in Asia and Latin America, and soon almost no country with endemic malaria was without drug-resistant parasites. In the late 1990s and early 2000s partnership-based aid programs, such as the Multilateral Initiative on Malaria and the Malaria Vaccine Initiative, were established to support the fight against malaria. Some of these programs aim to fund a broad range of malaria research, whereas others aim to fund ongoing malaria control efforts in endemic areas. These control efforts, which are the focus of antimalarial strategies established by the WHO, include the dissemination of insecticide-treated netting, the provision of prophylactic drugs to pregnant women, and earlier and more effective treatment of clinical cases, preferably through the use of multidrug “combination therapy” in order to attack drug-resistant parasites.
In the early 21st century, declining numbers of malaria cases and deaths suggested that efforts to control the disease were working. In 2011 officials estimated that, if control efforts were sustained, malaria could be eliminated from one-third of all affected countries within a decade.
Evolution of malaria parasites in primates
The malaria parasites of humans are thought to have evolved in tropical Africa from 2.5 million to 30 million years ago (P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae are among the oldest of the group). Scientists suspect that the human-specific parasites in existence today diverged from ancient lineages that infected early apes.
One of the first species of malaria parasites to be discovered in primates (other than humans) was P. reichenowi, which occurs in both chimpanzees and gorillas. This organism, first described between 1917 and 1920, was found to be very similar morphologically to P. falciparum, suggesting that the two must be closely related. However, subsequent studies conducted in the 1920s and '30s demonstrated that the two parasites appeared to be host-specific: P. falciparum could not infect chimpanzees, nor could P. reichenowi infect humans. This finding indicated that there existed important differences between the organisms. In 2002 the full genomic sequence of P. falciparum was published, enabling scientists to more closely investigate its genetic history. According to what is known about the phylogenetic relationships of Plasmodium species, P. falciparum is the most recent of the human parasites, which may help to explain its greater virulence. Although it is widely accepted that P. falciparum and P. reichenowi share a common ancestor, research on the timing of their evolutionary divergence has led to various and often inconsistent conclusions.
In 2009 and 2010 several new strains of Plasmodium were discovered in captive and wild African gorillas and chimpanzees. These new strains included P. GorA and P. GorB, which were found in gorillas, and P. gaboni, which was found in chimpanzees. Gorillas in Africa were also found to be infected with P. falciparum, providing the first evidence that this organism is able to naturally infect a primate species other than humans. This discovery raised concern over the close interactions between humans and nonhuman primates in Africa, which appear to increase the potential for inter-species parasite transmission. In contrast to human parasites, the parasites occurring in wild African apes generally do not cause severe illness. It is presumed that the long evolutionary history between apes and Plasmodium has dampened parasite virulency.
Source: "Malaria." Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite, 2013.In terms of developing a presumed "immunity" to war, those in leadership positions provide themselves with varying types of escape routes by using the resources bought and paid for by the public. And in terms of immunity, if war... like malaria has been with humanity for long stretches of time, why is there no immunity, unless the so-called "peace" which we see today is the type of immunity that has been developed. Typically, when one nation is defeated, the losing leadership is permitted to retain their position and personal wealth even while the rest of the public suffers the aftermath of the war... and thus have some extended immunity to war. In those cases where a leader is asked to leave, they do so with enough money that will enable them to live a life of leisure, even if millions of others are left to fend for themselves.
Unfortunately, sickness, disease and injury provide avenues for acquiring money where health does not. The same goes for war. War can make some people quite rich at the expense of some peoples' lives, and is a loss that has become adopted into a acceptable moral code defended by philosophical perspectives aligned with personal interests for wealth, power, and social prestige. Peace provides a means for some people to acquire large fortunes just as war allows others to. No less, peace-resistant forms of military strategy have been developed for those war-mongering parasites who like the many glorifications of war and seek to place themselves in some military-related encyclopedia.
And with respect to the evolution of war seen in terms of escalations in war materials manufacturing, is their a "patient zero" to be discovered like a Typhoid Mary? Does war have an equivalent that needs to be addressed in order for the disease to be appropriately addressed? Would researchers and analysts be permitted to uncover such a source and then publish their findings, or is there so much money and far too many people involved with the circumstances of war, disease, poverty, etc., that they have become so institutionalized that the absence thereof would destabilize world economies? Would the situation result to reveal that there are those who want to perpetuate things as they are because they have learned to live quite well?
Again, as above, there is a need to review the following account of Typhoid Mary by appropriately substituting the general ideas of the content within the parameter of a peace/war discussion:
Typhoid Mary
byname of Mary Mallonborn September 23, 1869, Cookstown, County Tyrone, Ireland
died November 11, 1938, North Brother Island, Bronx, New York, U.S.
(Mary Mallon was a) famous typhoid carrier who allegedly gave rise to multiple outbreaks of typhoid fever.
Mary immigrated to the United States in 1883 and subsequently made her living as a domestic servant, most often as a cook. It is not clear when she became a carrier of the typhoid bacterium (Salmonella typhi). However, from 1900 to 1907 nearly two dozen people fell ill with typhoid fever in households in New York City and Long Island where Mary worked. The illnesses often occurred shortly after Mary began working in each household, but, by the time the disease was traced to its source in a household where she had recently been employed, Mary had disappeared.
In 1906, after six people in a household of 11 where Mary had worked in Oyster Bay, New York, became sick with typhoid, the home owners hired New York City Department of Health sanitary engineer George Soper, whose specialty was studying typhoid fever epidemics, to investigate the outbreak. Other investigators were brought in as well and concluded that the outbreak likely was caused by contaminated water. Mary continued to work as a cook, moving from household to household until 1907, when she resurfaced working in a Park Avenue home in Manhattan. The winter of that year, following an outbreak in the Manhattan household that involved a death from the disease, Soper met with Mary. He subsequently linked all 22 cases of typhoid fever that had been recorded in New York City and the Long Island area to Mary.
Again Mary fled, but authorities led by Soper finally overtook her and had her committed to an isolation centre on North Brother Island, part of the Bronx, New York. There she stayed, despite an appeal to the U.S. Supreme Court, until 1910, when the health department released her on condition that she never again accept employment that involved the handling of food.
Four years later Soper began looking for Mary again when an epidemic broke out at a sanatorium in Newfoundland, New Jersey, and at Sloane Maternity Hospital in Manhattan, New York; Mary had worked as a cook at both places. She was at last found in a suburban home in Westchester county, New York, and was returned to North Brother Island, where she remained the rest of her life. A paralytic stroke in 1932 led to her slow death six years later.
Mary claimed to have been born in the United States, but it was later determined that she was an immigrant. Fifty-one original cases of typhoid and three deaths were directly attributed to her (countless more were indirectly attributed), although she herself was immune to the typhoid bacillus.
Source: "Typhoid Mary." Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite, 2013.If both peace and war are environmentally adaptable to different "host" circumstances, unraveling the source may require the talents of different types of detectives.
Date of Origination: Friday, 10-Feb-2017... 06:00 AM
Date of initial posting: Thursday, 23-Feb-2017... 10:58 AM
Updated posting: Saturday, 31-March-2018... 12:13 PM